Vector Art vs. Raster Images: Comparison
In the digital design and graphics world, the choice between vector and raster images is significant because it greatly impacts the quality and versatility of visual creations. Vector vs raster images are two distinct approaches with their own set of advantages and limitations. Understanding the differences between these two formats is essential for anyone involved in graphic design, illustration, or digital art. This comparison delves into the core characteristics of vector vs raster, exploring their unique characteristics, use cases, and how each format affects the outcome. This exploration of vector vs raster images will provide clear guidance for smarter design decisions.
Table Of Content
- What is Vector Art?
- What are Raster Images?
- Comparison between Vector vs Raster Images
- File Sizes
- Adobe Illustrator
- Mathematical Formula
- Vector Format vs Bitmap Image
- Pixels Per Inch (PPI) vs Dots Per Inch (DPI)
- Detailed Image vs Solid Colors
- File Format
- Individual Pixels
- Key Differences Between Raster and Vector Images
- Common Vector File Types Used in Graphic Design and Illustration
- AI (Adobe Illustrator)
- EPS (Encapsulated PostScript)
- SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics)
- PDF (Portable Document Format)
- CDR (CorelDRAW)
- Color Pixels in Raster Images vs Vector Images
- Business Card Example
- Final Words
- FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
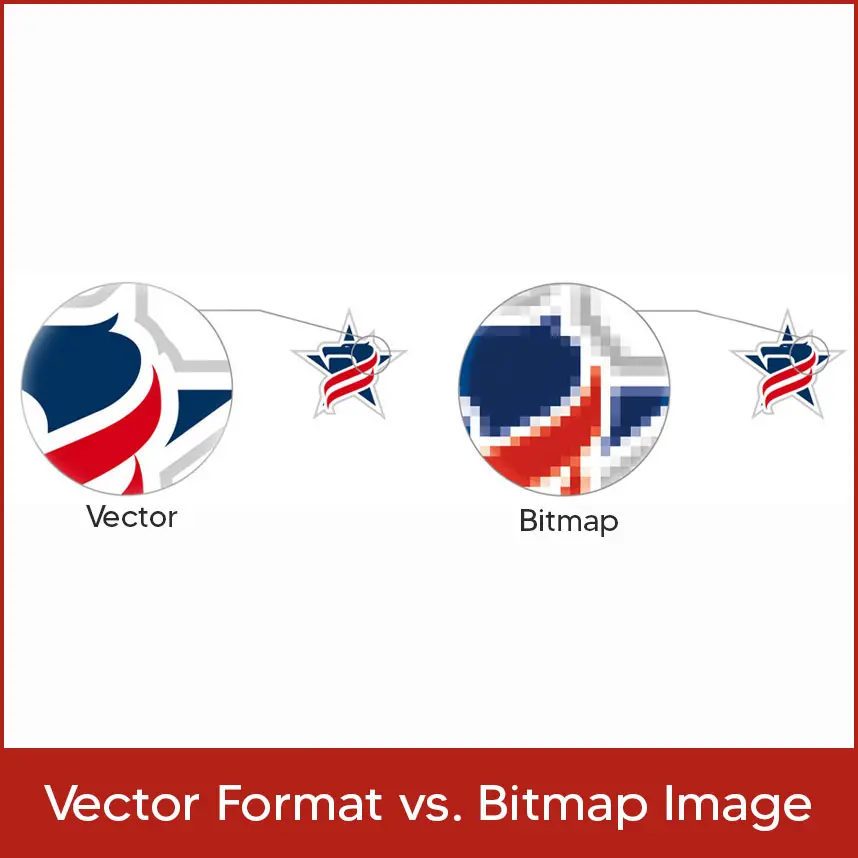
Vector art uses mathematical formulas to create shapes, lines, and colors. Unlike raster images, it can be scaled without losing quality. Programs like Adobe Illustrator are used to create vector graphics. It's perfect for logos, icons, and clean illustrations because of its sharp edges and flexibility. Raster images, or bitmaps, are made of tiny pixels on a grid. Each pixel holds a color, and when zoomed in, pixelation becomes visible. They're best for detailed photos, but they lose quality when enlarged. Common formats include JPEG, PNG, and TIFF. Vector files are smaller since they use formulas, not pixels. Formats like SVG and AI store shapes and lines. Raster images store data for each pixel, making file sizes larger. Compression helps reduce file sizes in raster images. Adobe Illustrator creates scalable vector graphics using formulas. It also converts raster images into vectors via “Image Trace." You can edit, resize, and apply effects without losing quality, making Illustrator ideal for logos and designs. Vector graphics use equations to define shapes and lines, allowing infinite resizing without quality loss. They maintain clarity at any size, unlike raster images, which become pixelated. These formulas also make vector files smaller and precise. Vector formats use formulas for sharp, scalable graphics, great for logos and text. Bitmap images use pixels, ideal for complex photos. Vectors scale cleanly; bitmaps risk losing clarity when resized. PPI is the pixel density in digital images; it affects image detail on screens. DPI is the printer's resolution for physical prints. PPI is editable via software; DPI is controlled by printers. Vectors are great for clean shapes and solid colors. Raster images are better for detailed, realistic visuals. While vectors are sharp and scalable, raster images capture smooth shading and textures better. Vector formats include SVG, AI, and EPS, scalable and editable. Raster formats like JPEG and PNG capture photo details but lose quality when resized. Some formats (e.g., PSD, AI) can include both vector and raster layers. Looking for professional help with converting raster images into scalable vector art? Digitizing USA provides vector tracing and raster-to-vector conversion services at affordable prices in the USA. Whether you're a designer, print shop owner, or embroiderer, we offer high-quality results and precise vectorization of your artwork. Our expert team ensures sharp, clean, and editable files that are perfect for logos, screen printing, or embroidery. Raster images use colored pixels. Enlarging them leads to blurriness or sharp edges. Adding pixels through software can distort quality. Vectors avoid this by using scalable formulas instead. Raster images are pixel-based and can lose quality when resized. They’re best for detailed images. Vector images are scalable and clean, ideal for logos and designs needing crisp edges. Choose based on project needs. When it comes to graphic design and illustration, several common vector file types are widely used. These file types are essential for preserving the scalability and quality of vector graphics. Here are some of the most popular vector file formats: AI files are the native format for Adobe Illustrator. They contain editable vector graphics and are widely used in the design industry. AI files are versatile and can be easily modified and resized without any loss in quality. EPS files are widely supported and can be used across different design programs. They can contain both vector and raster elements and are commonly used for printing purposes. SVG files are XML-based vector image files and have become popular for web design. All modern web browsers support them, and they can be easily resized and animated without losing quality. PDF files are widely used for sharing and printing vector graphics. They can contain vector and raster elements and are highly compatible across different platforms and devices. CDR files are the proprietary file format for CorelDRAW software. They are widely used in the graphic design industry for creating vector-based illustrations and designs. Understanding these common vector file types is essential for graphic designers and illustrators, as they ensure the preservation and compatibility of their work across different platforms and devices. Raster images use pixel grids to show color depth and realism. Each pixel adds detail. Vectors don’t rely on pixels; instead, they consist of scalable lines and shapes. They keep color sharpness at any size, but aren’t ideal for photos. Vector graphics are perfect for clean logos and text on business cards. They're scalable and sharp. Raster graphics work best for photos and color gradients but can blur when resized. Choose based on the design type. Why wait to upgrade your vector graphics? Digitizing USA offers fast turnaround time and delivers high-quality work to our customers across the USA. Our team brings your ideas to life with professional precision. Contact us today to get your vector conversion started and make your graphics stand out. Looking to create stunning visuals? Choose wisely between vector art and raster images. Vector art, crafted using mathematical formulas, promises limitless scalability while retaining crisp lines and sharp edges. Ideal for logos, icons, and illustrations, it's perfect for clean designs. On the flip side, raster images consist of pixels and excel in capturing complex photo details and smooth shading. Ready to upgrade your visuals? Our vector services can help you craft dynamic, versatile designs. Improve the quality and impact of your designs. Q1. What is vector art? Vector art is a type of graphic based on mathematical formulas to define shapes, lines, and colors. It can be resized without losing quality and is often used for logos, icons, and illustrations. Q2. How do raster images differ from vector art? Raster images are made up of pixels arranged on a grid, while vector art is composed of mathematical equations. Raster images lose quality when scaled up, while vector art can be resized without loss of quality. Q3. What advantages do vector images offer over raster images? Vector images are resolution-independent, meaning they can be scaled without compromising quality. They're ideal for creating graphics with clean lines, like logos and icons. Q4. What's the difference between Pixels Per Inch (PPI) and Dots Per Inch (DPI)? PPI refers to pixel density in a digital image, affecting its detail and sharpness. DPI indicates the printer's resolution, determining print quality. PPI can be adjusted with software, while DPI is set by the printer. Q5. How do vector vs raster graphics handle detailed images and solid colors differently? Vector graphics are great for solid colors, providing sharp lines and edges. Raster graphics excel at capturing complex details, textures, and soft color gradations. Vector images are best for simple shapes, while raster images are ideal for realism and detail.What is Vector Art?

What are Raster Images?

Comparison between Vector vs Raster Images
File Sizes
Adobe Illustrator
Mathematical Formula
Vector Format vs Bitmap Image
Pixels Per Inch (PPI) vs Dots Per Inch (DPI)
Detailed Image vs Solid Colors
File Format
Individual Pixels
Key Differences Between Raster and Vector Images
Common Vector File Types Used in Graphic Design and Illustration
.webp)
AI (Adobe Illustrator)
EPS (Encapsulated PostScript)
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics)
PDF (Portable Document Format)
CDR (CorelDRAW)
Color Pixels in Raster Images vs Vector Images
Business Card Example
Final Words
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)