
Common Client Questions About Vector Tracing – Answered
Table Of Content
- Q1: What is the primary benefit of using vector tools?
- Q2: What two things do you need for a vector?
- Q3: What file types work best with image trace?
- Q4: Can I convert any image into a vector file?
- Q5: Which techniques reduce errors and improve clean lines in vector tracing?
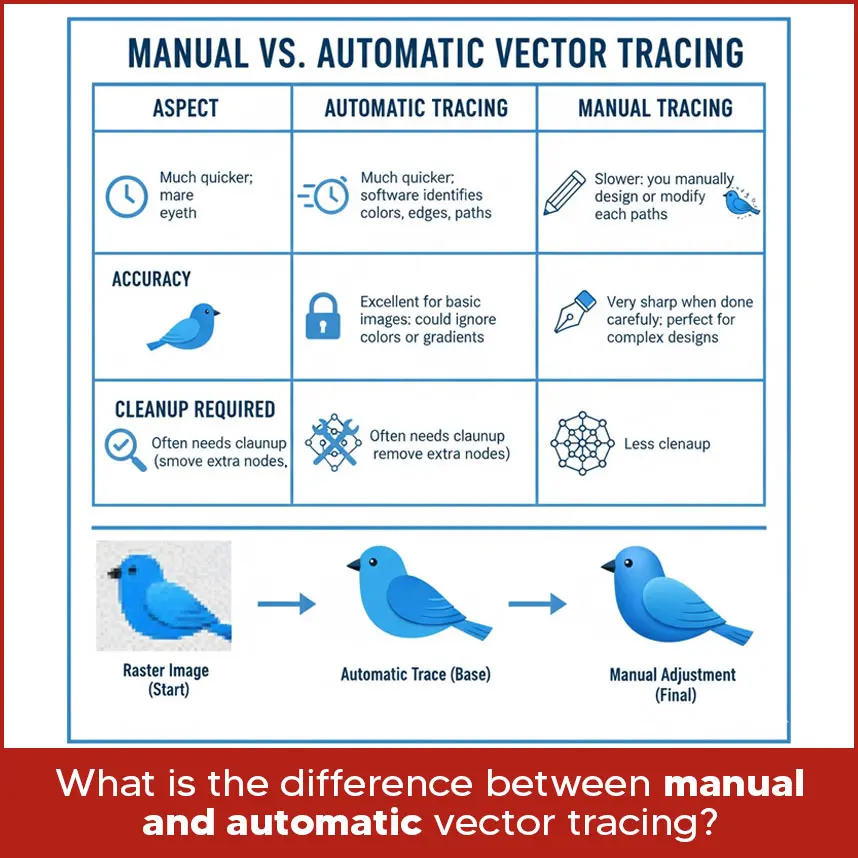
- Q6: What is the difference between manual and automatic vector tracing?
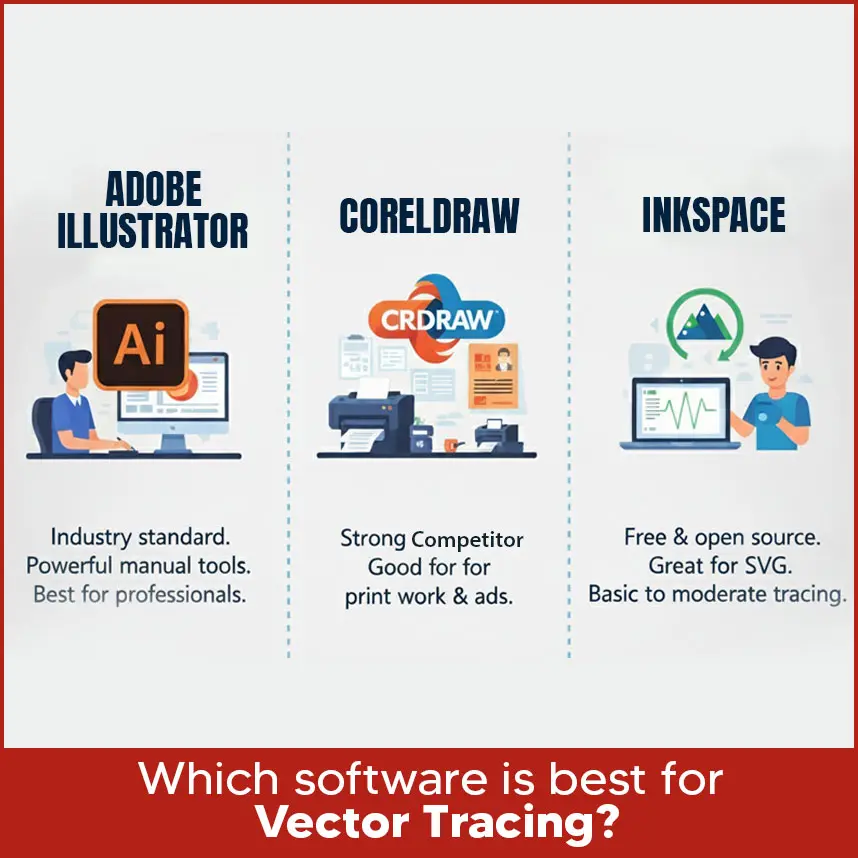
- Q7: Which software is best for vector tracing (Illustrator, CorelDRAW, etc.)?
- Q8: How long does vector tracing or raster to vector conversion usually take?
- Q9: What things should you consider when creating a vector?
- Q10: What is the most important thing about vector graphics?
- Q11: What are the two most commonly used vectors?
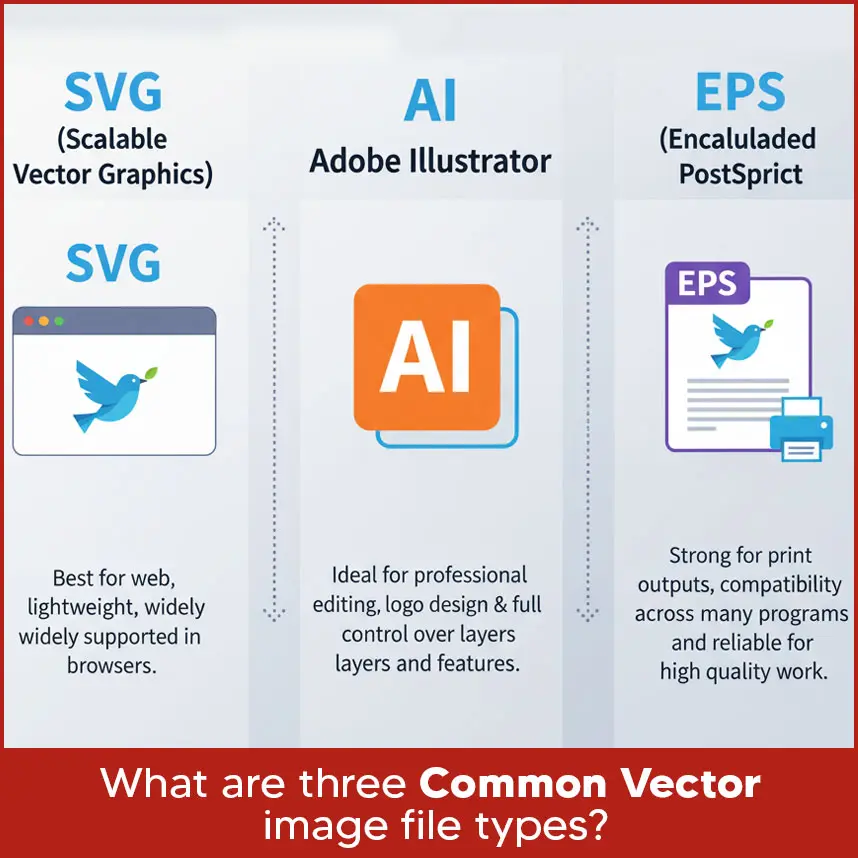
- Q12: What are three common vector image file types?
- Summary
Ah! We get so many questions related to vector tracing. Sometimes clients get confused about vector tracing software programs, files and many other important things. That's why we have decided to talk about the most common concerns and share solutions. So if you were searching for vector tracing solutions, you have come to the right place. Everyone wants images that scale smoothly, look professional & work for print and digital without losing quality. Basically pixel-based images can be transformed into sharp and scalable graphics using vector tracing, which maintains the image's high quality of detail whatever the scaling. We will address the most frequently asked queries about vector tracing so you can choose the best vector tracing service and must know what is right and wrong. Let's move forward with questions. The ability to resize images without affecting quality is the primary advantage of vector tools. It has become simpler to play with colors, modify shapes or select specific areas of an image when using vector tools. Vector graphics give flexibility without compromising quality, whether you're looking to create a logo for a website, billboard or shirt. To have a proper vector, you need: Anchor points (or nodes) and paths: These define the shape. Anchor points mark where a curve or line changes direction. Paths connect them. Fill and stroke attributes: You need information about inside color (fill) and outline color/width (stroke) so the shape looks exactly as designed. Without these two, the image either stops being a true vector (if you lose the anchor/path structure) or it looks wrong (if stroke/fill aren’t defined properly). When using “image trace” or similar tools, you start with a raster image. The best input formats are those that preserve detail and have low compression artifacts. So, formats like: PNG (lossless, good transparency). TIFF (high quality). BMP (rarely used now but acceptable if high resolution). JPEG, but only if it's high resolution and saved without too much compression. These give better results because “trace” tools try to identify edges and changes in color; fuzzy or compressed images make it harder. A large number of photos can be converted to vector files, although their final look varies depending on several factors: Image quality: Sharp edges, high resolution and distinct contrast are ideal. If the image is small or blurry, vector tracing gives results in rough or unclear edges. Complexity: Basic images, text or logos trace easily. It's more difficult to take highly detailed pictures with a lot of shading, minor texture or color changes. Sometimes simplifying or starting from scratch is preferable. Colors and gradients: These are harder. Some vector formats and software support gradients, but “tracing” tools may struggle. It may require manual cleanup after the auto-trace. So yes, you can, but expect some cleanup or simplification in many cases. To get clean, accurate vector results, these techniques help: 1. Start with a high resolution image. More pixels give more detail and sharper details make vector tracing smoother and help avoid jagged edges. 2. Increase contrast between subject and background. If there’s a sharp edge, the tracing tool picks it up better. 3. Use manual tracing (pen tool) for curved or complex shapes rather than relying fully on automatic tracing. Manual tracing gives control. 4. Simplify the image: reduce blurriness, remove unnecessary details, smooth gradients or textures if possible. 5. Refine anchor points carefully: if you add too many points, the edges may look uneven. If you use too few, the shapes can appear stiff. Here is how manual and automatic tracing compare: Often the best results come from combining both: use automatic tracing to get a base, then adjust manually for clean lines and accuracy. Here are some of the top software people use: Adobe Illustrator: Industry standard. Perfect tracing tool, good support for many formats and powerful manual tools. Best for professionals. CorelDRAW: Strong competitor, especially good for print work, ads and traditional design. Its native file formats (like CDR) work well. Inkscape: Free and open source. Great for small to medium-scale work; works well with SVG. For basic to moderate vector tracing, it’s highly capable. Other tools or plugins: Some specialized tools or add-ons target vector tracing. They can help with specific tasks (e.g. batch tracing or adjusting strokes automatically). Choice depends on what you need. If you work with professional print, Illustrator or CorelDRAW gives the best results; for simpler work or low budget, Inkscape or other more affordable tools can serve well. Auto tracing is not recommended because it gives poor results and mostly needs a lot of fixing afterward. Manual tracing is always the better option if you want clean and professional designs. The time it takes depends on how complex your design is. For simple artwork, manual tracing can be done in a few hours, while very detailed designs with many curves, colors or textures can take several hours or even 1 to 2 days to complete. But if you are on a deadline, Digitizing USA is the right choice. We provide raster to vector conversion/vector tracing services with a fast turnaround of 2 to 12 hours, even without compromising on quality. That’s why many clients trust us when they need accurate results quickly. When you or your designer makes a vector, keep these in mind: Is it meant for print, the web or large format? Resolutions and color modes (CMYK for print, RGB for web) differ depending on the output. Required file formats: Choose the appropriate type of file (AI, EPS, SVG, PDF, etc.) based on what you want to use it for. Scalability: Design so that when elements are enlarged, they stay clean. Avoid too many small details as they may get lost in quality or look messy when scaled. Simplicity: Clean lines, fewer nodes, simpler shapes generally produce better results and easier edits. Color and contrast: Good contrast helps tracing tools and support readability. If using many colors, make sure consistency. Compatibility: If others (printers, designers) need to use your file, choose widely supported formats. The most important thing is scalability or resizing without losing quality. That feature separates vector graphics from raster images. If you want small icons or large designs for billboards, right vector graphics will always remain sharp and will not lose their quality. Also, ease of editing is so important. If you or someone else needs to make changes like color, shape or layout, a well-constructed vector file saves time and delivers consistent results. The phrase “two most commonly used vectors” refers to two main types of use. Usually those are: Logos / Symbols: Simple shapes, brand identity graphics that need to scale well, used in many contexts. Illustrations / Icon: More detailed artwork, sometimes with curves, shadows, finer lines, used for apps, websites & print. Also you could say the two most common file types are used: for web (SVG) and for print / professional editing (AI or EPS). Here are three most common vector file types and what they are good for: SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics): Best for web, lightweight, widely supported in browsers. AI (Adobe Illustrator): Ideal for professional editing, logo design & full control over layers and features. EPS (Encapsulated PostScript): Strong for print outputs, compatibility across many programs and reliable for high quality work. Inshort vector tracing solutions give you a way to transform blurry images into scalable, clean graphics that work across print, digital and large formats even without losing quality. Once you know the file types, techniques, software and timing, you can make better decisions when designing or getting services. If you want reliable work, Digitizing USA delivers quality vector tracing services with fast turnaround times, unlimited revisions and affordable pricing. No matter you have a simple logo or a detailed design, we are experts in converting low quality designs into sharp & best quality without losing details. So if you have designs that need sharpness, professional vector work, feel free to reach out to us. You’ll get the best service and peace of mind.Q1: What is the primary benefit of using vector tools?
Q2: What two things do you need for a vector?
Q3: What file types work best with image trace?

Q4: Can I convert any image into a vector file?
Q5: Which techniques reduce errors and improve clean lines in vector tracing?
Q6: What is the difference between manual and automatic vector tracing?
Q7: Which software is best for vector tracing (Illustrator, CorelDRAW, etc.)?
Q8: How long does vector tracing or raster to vector conversion usually take?
Q9: What things should you consider when creating a vector?
Q10: What is the most important thing about vector graphics?

Q11: What are the two most commonly used vectors?

Q12: What are three common vector image file types?
Summary










